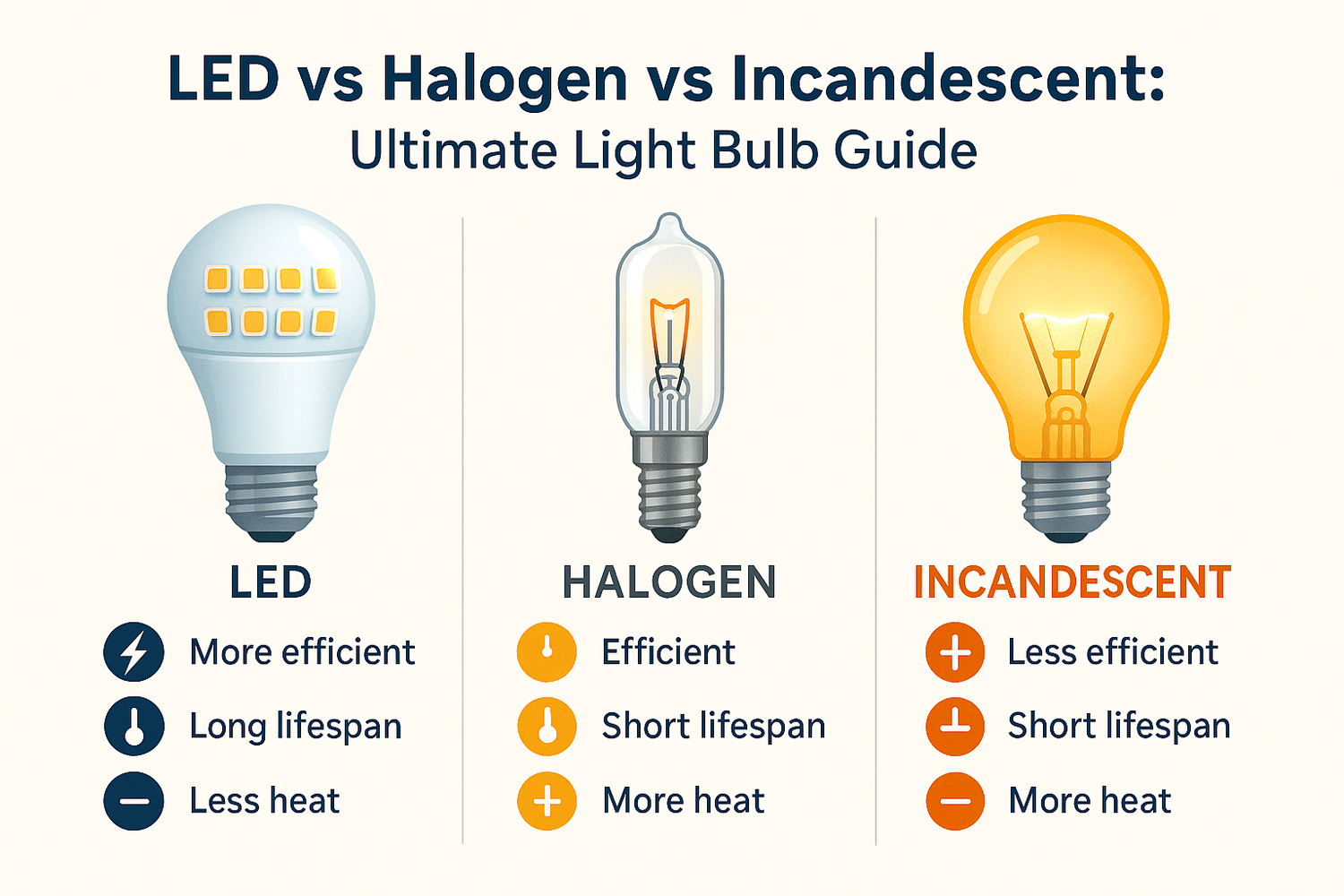
If you want the most energy efficient choice for your home, LED bulbs stand out. LEDs use about 80% less energy than halogen bulbs and can last up to 25,000 hours or more, while incandescent bulbs usually last around 1,000 hours. Halogen bulbs give off a bright light but use more power and do not last as long. The table below shows a quick light bulb types comparison, making it easy to see why LEDs are the smart pick for saving energy and money.
|
Bulb Type |
Lifespan (hours) |
Energy Use |
Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
|
LED |
Up to 25,000 |
Low |
Energy-efficient, long-lasting, cooler |
|
Halogen |
Around 2,000 |
Moderate |
Brighter than incandescent, more heat |
|
Incandescent |
Around 1,000 |
High |
Warm light, shortest lifespan, high energy use |
Key Takeaways
- LED bulbs use up to 80% less energy and last much longer than halogen and incandescent bulbs, saving you money and effort.
- Halogen bulbs provide bright, crisp light and work well with dimmers but use more energy and get hot quickly.
- Incandescent bulbs offer a warm, familiar glow but have the shortest lifespan and highest energy use, making them less efficient.
- Choosing bulbs by lumens (brightness) instead of watts helps you find the right light while saving energy.
- LED bulbs come in many colors and styles, often support smart controls, and stay cool, making them safe and versatile.
- Switching to LED bulbs can cut your energy bills significantly and reduce the frequency of bulb replacements.
- Consider your lighting needs, fixture compatibility, and budget to pick the best bulb type for each room or use.
- Recycling LED bulbs is safer and better for the environment since they contain no hazardous materials compared to some other types.
Light Bulb Types Comparison
Specs Table
When you look at a light bulb types comparison, you want to see how each option performs in real-world use. The table below shows the main differences between LED, halogen, and incandescent bulbs. You can quickly spot which bulb gives you the most light for the least energy and which one lasts the longest.
|
Bulb Type |
Typical Wattage (W) |
Typical Lumens |
Lumens per Watt |
Average Lifespan (hours) |
Average Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
LED |
4 - 9 |
720 - 800 |
80 - 100 |
15,000 - 30,000 |
Varies |
|
Halogen |
29 - 72 |
450 - 1600 |
15 - 22 |
2,000 |
Varies |
|
Incandescent |
40 - 100 |
450 - 1600 |
10 - 17 |
1,000 |
Varies |
Tip: If you want the brightest light with the lowest energy use, LEDs stand out in any light bulb types comparison.
Pros and Cons
You need to weigh the pros and cons when you make a light bulb types comparison. Each bulb type has unique strengths and weaknesses. Here is a simple breakdown to help you decide:
LED Bulbs
- Use much less energy than other bulbs.
- Last up to 30 times longer than incandescent bulbs.
- Stay cool to the touch, even after hours of use.
- Offer many color and brightness options.
- Cost more up front, but you save money over time.
Halogen Bulbs
- Give off a bright, crisp light that works well for task lighting.
- Turn on instantly and work with most dimmers.
- Use less energy than incandescent bulbs, but much more than LEDs.
- Get hot quickly, which can be a safety concern.
- Need to be replaced more often than LEDs.
Incandescent Bulbs
- Provide a warm, familiar glow that many people like.
- Cost very little to buy.
- Use the most energy and burn out quickly.
- Need frequent replacement, which adds up over time.
- Not as widely available now due to energy regulations.
When you compare these options side by side, you see that LED bulbs lead in almost every light bulb types comparison. You get more light for your money, fewer trips to the store for replacements, and lower energy bills. Halogen bulbs work well if you want instant, bright light and do not mind changing bulbs more often. Incandescent bulbs still offer a classic look, but they fall behind in efficiency and lifespan.
If you want to make the best choice for your home, always start with a clear light bulb types comparison. This approach helps you match your needs with the right technology and avoid wasting money or energy.
Light Bulb Types
LED
You will find that LED bulbs have changed the way people think about lighting. These bulbs use advanced technology to deliver bright light while using very little energy. You can save money on your electricity bill because LEDs consume up to 75% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs. Most LED bulbs last for 25,000 hours or more, so you will not need to replace them often. This long lifespan means less hassle and lower maintenance costs.
LED lighting stays cool, even after hours of use. This feature makes your home safer by reducing the risk of burns or fire. You can choose from many colors and styles, which gives you flexibility for any room or mood. Many LED bulbs work with smart home systems, so you can control your lights with your phone or voice. Some LEDs produce a single color, which is great for signs or displays. Others offer a full spectrum of light, perfect for general lighting in homes, offices, or outdoor spaces. RGB LEDs let you change colors for parties or special events.
You will see LED lighting in homes, businesses, and even factories. People switch to LEDs because they want better efficiency and sustainability. If you want a bulb that saves energy, lasts a long time, and offers many options, LED lighting is a top choice among all light bulb types.
- Highly energy-efficient, using up to 75% less energy than incandescent bulbs.
- Long lifespan, often 25,000 hours or more.
- Produces very little heat, making it safer.
- Available in many colors and styles.
- Works with smart technology for easy control.
- Used in homes, offices, outdoor spaces, and entertainment venues.
Halogen
Halogen bulbs give you a bright, crisp light that works well for tasks like reading or cooking. These bulbs use a special gas that helps them shine brighter than standard incandescent bulbs. You will notice that halogen bulbs turn on instantly and work with most dimmer switches. This makes them a good choice if you want adjustable lighting.
Halogen bulbs use less energy than incandescent bulbs, but they still use more than LEDs. They get hot quickly, so you need to be careful when touching them. You will need to replace halogen bulbs more often than LEDs, but less often than incandescent bulbs. Many people use halogen bulbs in desk lamps, spotlights, and under-cabinet lighting. If you want a bulb that offers bright light and works with dimmers, halogen bulbs are a solid option among light bulb types.
Incandescent
Incandescent bulbs have been around for over a century. You might recognize their warm, familiar glow. These bulbs cost less to buy, but they use the most energy and burn out quickly. Most incandescent bulbs last about 1,000 hours, so you will need to replace them often.
You will find incandescent bulbs in many shapes, but the standard A-shape is the most common. People use them in living rooms, bedrooms, and kitchens. Some choose incandescent bulbs for decorative lighting or when they want a specific color temperature. These bulbs work well with older dimming systems and are easy to dispose of. However, many people now switch to LED or halogen bulbs because of energy regulations and better efficiency.
|
Defining Characteristics of Incandescent Bulbs |
Common Applications and Market Insights |
|---|---|
|
Commoditized product, mainly by wattage, base type, and lifespan. |
Primarily used in residential indoor lighting, segmented by room type. |
|
Mostly A-shaped bulbs; some globe and candle shapes. |
Also used in commercial and industrial sectors, though less common. |
|
Favored for lower initial cost. |
Replacement demand driven by retrofitting older fixtures. |
|
Simple technology, easy disposal. |
Decorative lighting and applications valuing warm light output. |
|
Superior dimming capabilities. |
Market shrinking due to energy efficiency regulations. |
|
Warm light output preferred by some consumers. |
Production concentrated in Asia; consumption declining. |
Specialty Bulbs
When you look beyond standard bulbs, you find a wide range of specialty bulbs. These bulbs serve unique purposes and help you solve specific lighting needs. You can use them in cars, smart homes, plant growth, or decorative fixtures. Let’s explore some of the most common specialty bulbs you might encounter.
Automotive Bulbs
You rely on automotive bulbs every time you drive at night or in bad weather. These bulbs power your headlights, brake lights, turn signals, and interior lights. Most cars use halogen or LED bulbs for headlights. Halogen bulbs give you a bright, white light and cost less to replace. LED automotive bulbs last longer and use less energy, so you do not need to change them as often.
Tip: If you want better visibility and longer life for your car lights, consider upgrading to LED automotive bulbs.
You should always check your vehicle’s manual before buying replacement bulbs. Some cars need specific sizes or types.
Smart Bulbs
Smart bulbs let you control your lighting with your phone, tablet, or voice assistant. You can turn lights on or off, dim them, or even change their color without getting up. Many smart bulbs connect to Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, so you can set schedules or control them when you are away from home.
- You can create different moods for movie nights or parties.
- Some smart bulbs work with popular systems like Alexa, Google Assistant, or Apple HomeKit.
Smart bulbs often use LED technology, which means you get energy savings and a long lifespan. If you want convenience and flexibility, smart bulbs are a great choice.
Full Spectrum Bulbs
Full spectrum bulbs mimic natural sunlight. You use them when you want to see colors accurately or help plants grow indoors. Artists, photographers, and people who work with color often choose full spectrum bulbs for their workspaces. These bulbs can also help improve your mood during winter months when sunlight is limited.
|
Use Case |
Benefit |
|---|---|
|
Indoor gardening |
Supports healthy plant growth |
|
Art studios |
Shows true, vibrant colors |
|
Home offices |
Reduces eye strain |
You can find full spectrum bulbs in both LED and fluorescent options.
Candelabra Bulbs
Candelabra bulbs have a small base and a decorative shape. You often see them in chandeliers, wall sconces, or decorative lamps. These bulbs add style and elegance to your home. You can choose from LED, incandescent, or halogen candelabra bulbs, depending on your fixture and lighting needs.
Note: Always check the size and wattage before buying candelabra bulbs for your fixture.
Candelabra bulbs come in different shapes, such as flame-tip or torpedo, to match your décor. If you want to add a touch of charm to your space, candelabra bulbs are a perfect fit.
Energy Efficiency Comparison

Watts vs Lumens
When you shop for light bulbs, you often see two important numbers: watts and lumens. Watts measure how much electricity a bulb uses. Lumens measure how much light the bulb gives off. Years ago, you might have picked a bulb based on watts alone. Today, you should look at lumens to know how bright a bulb will be.
A higher wattage does not always mean a brighter bulb. For example, a halogen bulb that uses 40 watts produces about 500 lumens. This means it uses a fair amount of power to create a moderate amount of light. Modern bulbs, like LED lighting, can produce the same brightness with much less energy. You get more light for every watt you use.
|
Bulb Type |
Wattage (Watts) |
Lumens |
|---|---|---|
|
Halogen |
40 |
500 |
When you compare bulbs, always check both the wattage and the lumens. This helps you find the most efficient option for your needs.
LED Efficiency
LED bulbs have changed the way you think about lighting. These bulbs use advanced technology to turn most of the electricity they use into light, not heat. This makes them the leader in any energy efficiency comparison. You can get the same brightness as a traditional bulb while using a fraction of the power.
For example, an LED bulb that uses only 8 watts can produce as much light as a 60-watt incandescent bulb. This means you save energy every time you turn on the light. LED lighting also lasts much longer, so you do not need to replace bulbs as often. You will notice lower electricity bills and fewer trips to the store.
LEDs work well in almost any setting. You can use them in lamps, ceiling fixtures, or even outdoor lights. Many people choose LED lighting for its energy savings and long lifespan. When you want the best energy efficiency comparison, LED bulbs stand out as the top choice.
Halogen Efficiency
Halogen bulbs offer a step up from traditional incandescent bulbs. They use a special gas that helps them burn brighter and last longer. However, when you look at an energy efficiency comparison, halogen bulbs still use more power than LEDs.
A typical halogen bulb uses more watts to produce the same amount of light as an LED. For example, a 40-watt halogen bulb gives you about 500 lumens. You get a crisp, white light, but you pay for it with higher energy use. Halogen bulbs also get hot quickly, which means more energy turns into heat instead of light.
You might choose halogen bulbs if you want instant, bright light and compatibility with dimmers. However, if you want to maximize energy savings, LED lighting remains the better option.
Incandescent Efficiency
When you look at an energy efficiency comparison, incandescent bulbs stand out for their low efficiency. These bulbs use a thin wire filament that heats up and glows to produce light. Most of the electricity turns into heat, not light. This means you waste a lot of energy every time you flip the switch.
Incandescent bulbs usually last about 1,000 hours. You will find yourself replacing them often, especially if you use them in rooms where lights stay on for long periods. The warm glow feels cozy, but the high energy use adds up quickly. For example, a 60-watt incandescent bulb uses much more power than an LED that gives off the same amount of light.
You might notice that incandescent bulbs cost less to buy at first. However, the frequent replacements and higher electricity bills make them more expensive over time. If you want to save money and reduce your energy use, switching to more efficient bulbs makes a big difference.
Note: Incandescent bulbs convert only about 10% of the energy they use into visible light. The rest becomes heat, which can make rooms warmer and increase cooling costs in the summer.
|
Bulb Type |
Lifespan (hours) |
Energy Savings vs Incandescent |
|---|---|---|
|
Incandescent |
~1,000 |
0% |
|
Halogen |
~2,000 |
~30% |
|
LED |
15,000–50,000 |
Up to 90% |
You can see from the table that incandescent bulbs lag behind in both lifespan and efficiency. If you want to lower your energy bills and make fewer trips to the store, consider switching to a more efficient option.
Real-World Savings
You might wonder how much you can actually save by switching from incandescent or halogen bulbs to LEDs. The answer is impressive. If you replace ten 60-watt incandescent bulbs with LED equivalents, you can save $300 or more each year on your electricity bill. This shows how much energy savings add up when you make the switch.
Let’s look at a simple example. Imagine you use a 100-watt incandescent bulb for six hours every day. If you switch to a 10-watt LED that gives the same brightness, you save about £53 per year for just one bulb. The payback time is less than two months. The savings grow even more if you replace several bulbs in your home.
|
Bulb Type |
Power (W) |
LED Equivalent (W) |
Daily Use (hrs) |
Estimated Annual Savings (£) |
Payback Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Incandescent |
100 |
10 |
6 |
~53 |
Less than 2 months |
|
Halogen |
50 |
5 |
6 |
~26 |
Less than 2 months |
You also save money on replacement costs. LEDs last much longer than incandescent bulbs, so you buy fewer bulbs over time. This means you spend less on both energy and maintenance.
When you compare the options, you see that LEDs offer the best value for your money. You get lower energy bills, fewer replacements, and a quick return on your investment. Making the switch is one of the easiest ways to boost your home's energy efficiency and save money year after year.
Lifespan and Durability
Average Lifespan
When you choose a light bulb, lifespan matters. You want a bulb that lasts, so you do not have to replace it often. Manufacturers rate the average lifespan of each bulb type. LEDs lead the way, offering a much longer service life than older technologies. Most LED bulbs last around 25,000 hours. You can use them for years before needing a replacement. Incandescent bulbs, on the other hand, have a much shorter lifespan. The Phoebus cartel, a group of manufacturers from the early 20th century, set the standard for incandescent bulbs at about 1,000 hours. This short lifespan meant you had to buy new bulbs frequently. Today, incandescent bulbs average about 1,200 hours, which is still far less than LEDs. Halogen bulbs fall somewhere in between, but their lifespan is not much longer than that of incandescent bulbs. Many countries have phased out halogen bulbs because they do not meet modern efficiency standards.
Here is a quick look at the average rated lifespan for each type:
|
Bulb Type |
Average Rated Lifespan (hours) |
|---|---|
|
LED |
~25,000 |
|
Incandescent |
~1,200 |
|
Halogen |
Similar to incandescent |
You can see that LEDs last much longer. This means fewer bulb changes and less hassle for you.
Durability Factors
Durability goes beyond just how long a bulb lasts. You want a bulb that stands up to real-world use. Several factors affect how well a bulb performs over time.
- LED bulbs use advanced technology and strong materials. Many models, such as those rated IP67 or IP68, resist shocks, dust, and water. You can use them in harsh environments without worry. LEDs also run cooler and use less energy, which puts less stress on your home’s electrical system.
- Active cooling systems in some LED bulbs help keep temperatures steady. This prevents overheating and extends the bulb’s life.
- Halogen and incandescent bulbs do not handle tough conditions as well. Older sealed-beam headlights, which used these technologies, often suffered from yellowing, leaks, and breakage. Glass lenses sometimes resisted breaking, but metal reflectors could bend. Plastic parts often yellowed or leaked, leading to early failure.
- Halogen bulbs get hot quickly. High temperatures can cause the bulb to fail sooner, especially if you touch the glass with your fingers. Oils from your skin can create hot spots and shorten the bulb’s life.
- Incandescent bulbs have simple construction but are fragile. They break easily if dropped or bumped.
Tip: If you want a bulb that lasts through storms, vibrations, or frequent switching, choose an LED. Their robust design and weather resistance make them a smart pick for both indoor and outdoor use.
You get more value and peace of mind when you pick a bulb that combines a long lifespan with strong durability. LEDs stand out in both areas, making them a reliable choice for your lighting needs.
Cost Breakdown
Upfront Cost
When you shop for light bulbs, you notice that LED bulbs usually cost more than halogen or incandescent bulbs. You might pay $2 to $8 for a single LED bulb. Halogen bulbs often cost between $1 and $3 each. Incandescent bulbs are the cheapest, sometimes less than $1 per bulb. This price difference can make you wonder if LEDs are worth it.
However, you should remember that the upfront cost is only part of the story. LEDs last much longer than other bulbs. You buy them less often, which saves you money over time. If you want to light your home for years without frequent replacements, paying a little more at the start makes sense.
|
Bulb Type |
Typical Upfront Cost (USD) |
Average Lifespan (hours) |
|---|---|---|
|
LED |
$2 – $8 |
15,000 – 30,000 |
|
Halogen |
$1 – $3 |
2,000 |
|
Incandescent |
<$1 |
1,000 |
Long-Term Cost
You need to look beyond the price tag to see the real value. Over several years, the total cost of lighting includes not just the price of the bulb, but also how much electricity it uses and how often you need to replace it. LEDs use much less energy than halogen or incandescent bulbs. This means your electricity bill drops when you switch to LEDs.
Let’s do a quick cost comparison. If you use an LED bulb for 25,000 hours, you might only need to buy one bulb. For the same amount of light, you would need to buy about 12 halogen bulbs or 25 incandescent bulbs. The cost of replacements adds up fast. You also spend more on electricity with halogen and incandescent bulbs. Over 10 years, LEDs can save you hundreds of dollars in both energy and replacement costs.
ROI Calculator
You might wonder how long it takes to recover the higher upfront cost of an LED bulb. Most homeowners see a payback period of about 1 to 2 years. This quick return comes from lower energy bills and fewer bulb replacements. For example, LED pool lights last 15 to 25 years, while incandescent bulbs last only 1 to 2 years. LEDs also use 75–80% less electricity than incandescent bulbs. These savings add up every month.
💡 Tip: If you replace ten 60-watt incandescent bulbs with LED bulbs, you can save around $300 per year on your electricity bill. The savings grow even more if you switch out more bulbs.
Here is a simple ROI calculator table for a single bulb over 5 years:
|
Bulb Type |
Upfront Cost |
Replacement Cost (5 yrs) |
Energy Cost (5 yrs) |
Total Cost (5 yrs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
LED |
$5 |
$0 |
$10 |
$15 |
|
Halogen |
$2 |
$8 |
$25 |
$35 |
|
Incandescent |
$0.75 |
$24 |
$40 |
$64.75 |
You see that LEDs cost more at first, but you save money quickly. After about two years, the savings from lower energy use and fewer replacements cover the higher upfront cost. Over five to ten years, LEDs offer the best value for your money.
Brightness and Color
Lumens and Color Temperature
When you choose a light bulb, you want to know how bright it will be and what kind of light it gives off. The two main things to look at are lumens and color temperature. Lumens measure the brightness of a bulb. The higher the lumens, the brighter the light. Color temperature, measured in Kelvin (K), tells you if the light looks warm or cool. Warm light (around 2700K) feels cozy and soft. Cool light (5000K or higher) feels crisp and energizing.
Here is a quick table to help you compare the typical brightness and color temperature options for different bulb types:
|
Bulb Type |
Typical Lumen Output Range |
Color Temperature Options (Kelvin) |
Key Characteristics and Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
LED |
400 - 800 lumens |
Warm (2700K-3000K), Neutral (3500K-4100K), Cool (5000K-6500K) |
Energy-efficient, long lifespan, cooler operation |
|
Halogen |
Similar to incandescent, generally bright |
Warm to cool spectrum, better color rendering than incandescent |
Brighter than incandescent, moderate lifespan, generates heat |
|
Incandescent |
Typically lower lumen output compared to LED and halogen |
Warm light (around 2700K) |
Warm, natural light, inexpensive upfront, short lifespan |
💡 Tip: Always check the lumens on the package to know the real brightness, not just the wattage.
LED Options
You have many choices when it comes to led bulbs. These bulbs come in a wide range of brightness levels and color temperatures. For example, you can find a small led bulb that gives off 350 lumens, perfect for a bedside lamp. You can also find a powerful led bulb that produces up to 3750 lumens, which works well in large spaces or for outdoor lighting.
Led bulbs let you pick the color of light you want. You can choose warm white (2700K-3000K) for a cozy living room or cool white (5000K) for a bright kitchen. Some led bulbs even let you change the color with a remote or app. This flexibility makes it easy to match the lighting to your mood or activity.
|
Product Example |
Wattage |
Brightness (Lumens) |
Color Temperature (K) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
TCP 25W T-shape LED bulb |
25W |
3750 |
5000K (cool white) |
|
SATCO 4W T10 LED bulb |
4W |
350-450 |
2700K to 3000K (warm white) |
You can use led bulbs in almost any room. They work well for reading, working, or relaxing. You get the brightness you need and the color you like, all while saving energy.
Halogen Options
Halogen bulbs give you a bright, clear light that many people like for task lighting. Most halogen bulbs have a color temperature between 2700K and 3000K. This range creates a warm and inviting atmosphere, perfect for living rooms or bedrooms. You often see halogen bulbs in desk lamps, spotlights, and accent lighting.
Halogen bulbs usually match the brightness of incandescent bulbs but with a bit more efficiency. You get a strong, focused beam that helps you see details clearly. Many people choose halogen bulbs when they want good color rendering and a familiar warm glow.
Note: Halogen bulbs can get hot, so always handle them with care.
Incandescent Options
When you choose an incandescent bulb, you get a classic lighting experience. These bulbs have been around for over a century. You might remember the warm, inviting glow they create in living rooms and bedrooms. Incandescent bulbs produce light by heating a thin wire filament until it glows. This process gives you a soft, familiar light that many people still enjoy.
You will notice that incandescent bulbs come in a range of wattages. Each wattage level gives you a different level of brightness. For example, a 40-watt bulb provides a gentle light, while a 100-watt bulb offers much more brightness for larger spaces. You can use this flexibility to match the brightness to your needs in each room.
|
Wattage (W) |
Typical Brightness (Lumens) |
Common Use |
|---|---|---|
|
40 |
450 |
Nightstands, accent lamps |
|
60 |
800 |
Bedrooms, living rooms |
|
75 |
1100 |
Kitchens, work areas |
|
100 |
1600 |
Garages, large spaces |
You can easily adjust the brightness of incandescent bulbs with most dimmer switches. This feature lets you set the mood for any occasion. You might want a soft glow for movie night or full brightness for reading. The smooth dimming ability makes incandescent bulbs a favorite for many people who want control over their lighting.
Color temperature is another important factor. Incandescent bulbs usually have a color temperature around 2700K. This means you get a warm, yellowish light that feels cozy and comfortable. You will not find many options for cooler or daylight-like colors with incandescent bulbs. If you prefer a warm atmosphere, these bulbs work well.
Here are some quick tips for using incandescent bulbs to get the right brightness:
- Use higher wattage bulbs in areas where you need more brightness, like kitchens or garages.
- Choose lower wattage bulbs for softer brightness in bedrooms or hallways.
- Pair incandescent bulbs with dimmers to fine-tune the brightness for any activity.
💡 Tip: Always check the maximum wattage rating for your light fixture before installing an incandescent bulb. Using a bulb with too much brightness can overheat the fixture.
You might notice that incandescent bulbs do not offer as many choices for brightness and color as newer technologies. However, they still provide reliable, warm light that many people appreciate. If you want a simple way to control brightness and enjoy a classic look, incandescent bulbs remain a solid option.
Environmental Impact
Energy Use and Carbon Footprint
You make a big difference in your home's carbon footprint when you choose the right light bulb. LEDs stand out for their low energy consumption and long lifespan. You use up to 70% less energy with LEDs compared to traditional halogen or incandescent bulbs. This means you lower your electricity bills and reduce your impact on the environment. The longer lifespan of LEDs, often reaching 50,000 hours or more, means you replace bulbs less often. Fewer replacements mean less waste and fewer resources used for manufacturing and shipping.
- LEDs consume up to 70% less energy than halogen or incandescent bulbs.
- Longer lifespans mean fewer replacements and less waste.
- Lower energy consumption leads to reduced CO2 emissions over the bulb's life.
- LEDs do not contain toxic materials, making disposal safer for the environment.
You can see the differences in the table below:
|
Lighting Type |
Estimated Lifespan (hours) |
Energy Consumption (Watts) |
Environmental Impact Score (1-10) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Traditional (Halogen/Incandescent) |
1,500–7,000 |
80–250 |
2 |
|
LED Standard Model |
40,000–60,000 |
24–70 |
8 |
|
LED Advanced Smart Model |
55,000–100,000 |
12–45 |
10 |
Choosing LEDs helps you cut down on energy consumption and shrink your carbon footprint.
Materials and Recycling
You might wonder what goes into making your light bulbs and how you can recycle them. LED bulbs use semiconductor crystals and LED chips, often inside glass bulbs. Some advanced LEDs use graphene coatings to boost brightness and manage heat. Many LED products, especially those for tough environments, use recyclable materials and rugged designs. This focus on recyclability helps reduce e-waste and supports a cleaner planet.
Halogen and incandescent bulbs use tungsten filaments, glass envelopes, and inert gases. While you can recycle the glass and metal parts, these bulbs are not as eco-friendly as LEDs. You should always check local recycling guidelines before disposing of any bulb. By choosing LEDs, you support products designed for sustainability and easier recycling.
Hazardous Substances
You want to keep your home safe and protect the environment. LEDs do not contain hazardous substances. You can recycle most of their parts, and you do not need to worry about toxic materials. Halogen and incandescent bulbs also do not have hazardous chemicals, but you should handle them carefully to avoid broken glass. Fluorescent bulbs, which are not the focus here, do contain mercury and need special disposal.
Here is a quick comparison:
|
Bulb Type |
Hazardous Substances Present |
Environmental or Health Risks / Disposal Notes |
|---|---|---|
|
LED |
None hazardous; contains recyclable materials |
Not hazardous; recyclable materials should be collected separately. |
|
Halogen |
None hazardous |
Not easily recycled; should be disposed of in trash (landfill). |
|
Incandescent |
None hazardous |
No hazardous materials; care needed to avoid glass shards when disposing. |
|
Fluorescent |
Mercury vapor |
Mercury is hazardous; careful disposal required to avoid vapor release and glass shards. |
You can feel confident that using LEDs supports a safer and greener environment.
Compatibility and Use Cases
Dimmability
You may want to adjust the brightness of your lights to create the right mood or save energy. Incandescent bulbs make this easy. They work with most standard dimmer switches because they use a simple resistive load. You can dim them smoothly without worrying about flicker or color changes. Halogen bulbs also support dimming and usually work well with triac dimmers, just like incandescent bulbs. Manufacturers confirm that halogen bulbs are dimmable, so you can use them for adjustable lighting in many settings.
LED bulbs offer dimming too, but you need to pay attention to compatibility. LEDs require special dimmable drivers that decode signals from phase-cut dimmers. These drivers help prevent flickering and keep the color temperature steady as you dim the light. When you choose LED bulbs, check that both the bulb and the dimmer switch are compatible. Some smart dimmers add extra features, such as remote control and scene settings, but always match the dimmer type to your LED bulbs for the best results.
💡 Tip: For flicker-free dimming with LEDs, use bulbs and dimmers designed to work together.
Fixture Compatibility
You want your new bulbs to fit and work safely in your existing fixtures. Incandescent and halogen bulbs fit most standard fixtures, including under-cabinet lamps and can lights. LED bulbs are available as "drop-in" replacements for many incandescent types, making upgrades simple. Before you swap bulbs, check the voltage and wattage ratings on both the bulb and the fixture. This helps you avoid electrical issues.
Common fixtures include can lights, range hood fixtures, and under-cabinet lamps. Always verify the fixture’s size, trim type, and electrical connections. Inspect the fixture for any damage, especially if you are replacing older halogen bulbs, which can cause heat damage over time. For LED strips, you may need to replace the power supply with an LED driver and rewire the fixture.
|
Aspect |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Compatible Fixtures |
Can lights, range hoods, under-cabinet lamps |
|
Compatibility Considerations |
Check fixture size, trim, and wiring; inspect for damage before retrofit |
|
Common Issues |
Heat damage, improper fit, electrical incompatibility, outdated fixtures |
|
Safety Requirements |
Use certified kits; follow safety codes; ensure proper wiring |
|
Installation Best Practices |
Pre-check compatibility, follow safety standards, test after installation |
Best Uses by Room
Living Room
You want your living room to feel comfortable and inviting. LED downlights work well here because they provide flexible, energy-efficient lighting. You can use LED strip lights for accent lighting behind shelves or under furniture. If you prefer a classic look, incandescent bulbs give a warm glow, perfect for relaxing evenings.
Kitchen
In the kitchen, you need both bright and focused light. LED downlights offer general illumination, while LED strip lights under cabinets add safety and style. Spotlights, either halogen or LED, help you see clearly on kitchen islands, sinks, and cooktops. These options make food prep and cleaning easier.
Bathroom
Bathrooms need a mix of ambient and task lighting. Incandescent bulbs (2700-3000K) create a warm, relaxing atmosphere. For grooming or makeup, choose halogen or LED bulbs (3000-5000K) for clear, bright light. Daylight LED bulbs (5000K+) give you the best visibility for detailed tasks.
Outdoor
Outdoor spaces benefit from durable, weather-resistant lighting. LED bulbs last long and handle temperature changes well. Use LED floodlights for security, or LED strip lights to highlight walkways and landscaping. Always choose bulbs rated for outdoor use to ensure safety and performance.
🏡 Note: Matching the right bulb to each room helps you get the best lighting, comfort, and energy savings throughout your home.
LED vs CFL
Efficiency
When you compare led vs cfl, you notice big differences in how much energy each bulb uses. Led bulbs stand out for their low power consumption and strong light output. Recent laboratory tests show that led bulbs use up to 50% less power than cfl bulbs while giving you better illumination. You get more light for every watt you use. The International Energy Agency recommends led lighting because of its high efficiency and long-term savings. Many government programs in countries like India and China choose led bulbs for solar street lighting. They do this because leds are reliable and cost-effective.
Cfl bulbs, which belong to the fluorescent family, still appear in some homes and businesses. You might see them in places where the initial cost matters most. Cfl bulbs use less energy than old incandescent bulbs, but they cannot match the efficiency of led lighting. When you look at led vs cfl, you see that led bulbs help you save more on your electricity bill over time.
- Led bulbs consume up to 50% less power than cfl bulbs.
- Led bulbs provide better illumination and higher efficiency.
- Cfl bulbs remain common in low-income or off-grid areas due to lower upfront cost.
- Fluorescent lighting, including cfl, falls behind led in energy savings.
Lifespan
You want your bulbs to last as long as possible. Manufacturer data shows that led bulbs have an average lifespan of about 50,000 hours. This means you can use them for many years before needing a replacement. When you compare led vs cfl, you find that cfl bulbs, as a type of compact fluorescent, do not last as long as leds. Most cfl bulbs offer a lifespan between 8,000 and 15,000 hours. You will need to replace cfl bulbs more often, which adds to your maintenance costs.
Fluorescent bulbs, including cfl, can lose brightness over time. You might notice that your cfl bulbs start to flicker or take longer to reach full brightness as they age. Led bulbs keep their brightness much longer and do not suffer from these issues. If you want fewer bulb changes and less hassle, led bulbs give you a clear advantage in the led vs cfl debate.
Environmental Impact
You care about the environment and want to make smart choices. Led bulbs help you reduce your carbon footprint because they use less energy and last longer. You throw away fewer bulbs, which means less waste in landfills. Led bulbs do not contain hazardous materials, so you can recycle them safely.
Cfl bulbs, as part of the fluorescent family, contain small amounts of mercury. This makes disposal more complicated. If a cfl bulb breaks, you need to handle it carefully to avoid exposure to mercury vapor. Fluorescent lighting, including cfl, creates more waste over time because you replace these bulbs more often. When you compare led vs cfl, you see that led bulbs offer a safer and greener choice for your home.
🌱 Choosing led bulbs over cfl and other fluorescent options helps you save energy, reduce waste, and protect the environment.
How to Choose
Key Questions
Before you pick a light bulb, you should ask yourself a few important questions. These questions help you match your needs with the right type of bulb. Think about your space, your budget, and your lighting goals.
-
What is the main purpose of the light?
Do you need bright task lighting for a kitchen or soft mood lighting for a bedroom? -
How much do you want to spend up front?
Are you looking for the lowest initial cost, or do you want to save money over time? -
How often do you want to replace bulbs?
Do you prefer a long-lasting option, or does frequent replacement not bother you? -
Do you need special features?
Would you like smart controls, dimming, or color-changing options? -
Is energy efficiency important to you?
Are you trying to lower your electricity bill or reduce your carbon footprint?
💡 Tip: Write down your answers. This makes it easier to compare bulbs and choose the best one for your needs.
Step-by-Step Guide
You can follow these simple steps to choose the right light bulb for any room or fixture:
-
Check Your Fixture
Look at your light fixture. Find out what type of bulb base and wattage it supports. You can usually find this information on the fixture or in its manual. -
Decide on Brightness and Color
Think about how much light you need. Check the lumens on the bulb package. Choose a color temperature that fits the mood you want. Warm white (2700K) feels cozy. Cool white (5000K) feels bright and energizing. -
Pick the Bulb Type
Use your answers from the key questions. If you want energy savings and long life, choose LED. For instant bright light, halogen works well. If you like a classic look, incandescent gives a warm glow. -
Consider Special Features
Do you want smart controls or dimming? Make sure the bulb supports these features. Some LED bulbs work with apps or voice assistants. -
Compare Costs
Look at both the upfront price and the long-term savings. LEDs may cost more at first, but you save money on energy and replacements. -
Buy and Install
Purchase the bulb that fits your needs. Install it safely. Enjoy better lighting and lower bills!
📝 Note: Always recycle old bulbs properly. Check local guidelines for safe disposal.
By following these steps, you make a smart choice for your home and your wallet.
You now know that LED bulbs usually offer the best value for your home. LEDs use less energy, last much longer, and save you money over time compared to halogen or incandescent bulbs. Review your current fixtures and make a list of bulbs you want to upgrade. Use the comparison tables to guide your choices.
💡 Tip: Making the switch to LEDs helps you save money and protect the environment. You have the power to create a brighter, more efficient home!
FAQ
What is the main difference between LED, halogen, and incandescent bulbs?
You will notice that LED bulbs use less energy and last much longer than halogen or incandescent bulbs. Halogen bulbs shine brighter than incandescent bulbs but use more power. Incandescent bulbs give a warm glow but have the shortest lifespan.
Are CFL bulbs still a good choice for home lighting?
You can use cfl bulbs if you want to save energy compared to incandescent bulbs. However, LED bulbs now offer better efficiency and longer life. Many people switch from cfl to LED for lower electricity bills and less frequent replacements.
How does CFL vs incandescent compare for energy savings?
You save more energy with cfl bulbs than with incandescent bulbs. CFL bulbs use about 70% less electricity. When you compare cfl vs incandescent, you will see lower energy bills and fewer bulb changes with cfl.
Can I use CFL bulbs in any fixture?
You can use cfl bulbs in most fixtures, but always check the label. Some cfl bulbs do not work well in enclosed or dimmable fixtures. For best results, choose cfl bulbs designed for your specific fixture type.
How do CFL bulbs compare to LED bulbs?
You will find that cfl bulbs use less energy than incandescent bulbs but more than LED bulbs. LED bulbs last longer and turn on instantly. If you want the best efficiency, choose LED over cfl.
Are there any safety concerns with CFL bulbs?
You should handle cfl bulbs carefully because they contain a small amount of mercury. If a cfl bulb breaks, follow cleanup instructions and ventilate the area. Always recycle cfl bulbs at approved locations.
What should I consider when choosing between CFL, LED, and incandescent bulbs?
You should think about energy use, lifespan, and cost. CFL bulbs save more energy than incandescent bulbs. LED bulbs last the longest and use the least energy. When you compare cfl vs incandescent, cfl bulbs offer better efficiency.
Can I recycle CFL bulbs?
You can recycle cfl bulbs at many hardware stores or recycling centers. Do not throw cfl bulbs in the trash because of the mercury content. Recycling helps protect the environment and keeps your home safe.