Solar lights deliver significant environmental and economic benefits when compared to traditional lighting. Solar street lights almost eliminate operational carbon emissions, while traditional street lights emit up to 2 tons of CO2 per unit each year. The table below shows key differences:
|
Aspect |
Solar Street Lights |
Traditional Street Lights |
|---|---|---|
|
Annual CO2 Emissions |
Near zero |
1–2 tons per light |
|
Annual Energy Cost |
$0 |
$200–$400 |
|
Maintenance/Year |
$50–$100 |
$150–$300 |
Solar street lights offer a sustainable alternative by using renewable energy and reducing both energy costs and maintenance needs. These benefits make solar lights a smart choice for anyone seeking reliable, eco-friendly lighting.
Key Takeaways
- Solar street lights cut carbon emissions by over 90% compared to traditional grid-powered lights.
- They eliminate electricity costs and reduce maintenance expenses, saving money long-term.
- Solar lights use advanced LEDs and smart controls to provide efficient, targeted lighting with less energy waste.
- Installation is faster and cheaper since solar lights need no trenching or wiring.
- Solar lighting components are highly recyclable, reducing landfill waste and pollution.
- Government incentives and tax credits help lower the upfront cost of solar lighting projects.
- Solar lights work well in urban and rural areas, improving safety and supporting economic growth.
- Modern solar technology ensures reliable performance even in low sunlight and harsh weather conditions.
Solar Lights and the Environment
Carbon Emissions
Grid vs. Solar
Solar street lights offer a dramatic reduction in carbon emissions compared to traditional lighting. Traditional grid-powered lights depend on electricity generated from fossil fuels. Coal-fired power plants produce between 0.85 and 1.1 kg of carbon dioxide per kilowatt-hour, while gas-fired plants emit 0.35 to 0.5 kg per kilowatt-hour. On average, a single 100-watt traditional street light can generate up to 164 kg of carbon emissions each year. In contrast, solar street lights operate using renewable energy from the sun. They produce no emissions during daily operation. Over a five-year lifespan, a solar street light emits only 10–16 kg of carbon, mainly from manufacturing. This means solar street lights cut operational carbon emissions by over 90% compared to grid-powered lights.
The U.S. Department of Energy estimates that solar energy systems reduce carbon emissions by about 100 million metric tons annually in the United States. This reduction equals removing 21 million cars from the road for a year. Solar lights avoid emissions from both electricity use and frequent bulb replacements, making them a leading environmentally friendly option for sustainable lighting.
Life-Cycle Impact
Solar street lights provide environmental benefits throughout their entire life cycle. Traditional lighting systems contribute to carbon emissions not only during operation but also through frequent maintenance and bulb replacements. Solar street lights, on the other hand, require less maintenance and have longer-lasting components. Their use of renewable energy further reduces the environmental impact over time. By switching to solar street lights, communities can significantly lower their carbon footprint and support clean energy solutions.
Pollution and Sustainability
Traditional lighting systems create several types of pollution:
- Excessive brightness from operating at full power, regardless of need
- Poor directionality, causing light to scatter upward and sideways
- Light spectrums that disrupt biological cycles and contribute to sky glow
- Static operation without adaptive controls, leading to energy waste
- Sky glow, glare, light trespass, and clutter that harm ecosystems and human health
Solar street lights address these issues with advanced technology:
- They use renewable solar energy, eliminating reliance on fossil fuels and grid power.
- High-efficiency LEDs with precise optics direct light only where needed.
- Smart adaptive controls, such as motion detection and programmable timing, reduce unnecessary illumination.
- Dark-sky compliant designs prevent upward light emission and minimize light pollution.
- Independent operation reduces infrastructure needs and carbon emissions.
Solar street lights help conserve biodiversity by minimizing light pollution and protecting nocturnal wildlife. They also reduce environmental disturbance during installation, supporting sustainability in both urban and rural environments.
Solar street lights offer additional sustainability benefits:
- They reduce reliance on fossil fuels, lowering carbon emissions and supporting a greener environment.
- Municipalities benefit from lower electricity costs and reduced maintenance.
- Reliable illumination enhances safety and security, deterring crime and improving pedestrian safety.
- Solar street lights can be installed in remote or off-grid areas, expanding access to lighting.
- Advanced features like sensors and battery backups ensure consistent lighting during outages.
- Sleek designs improve urban aesthetics and promote green initiatives.
- Minimal maintenance and easy installation support sustainable infrastructure development.
Solar street lights operate independently of power grids, increasing resilience during extreme weather and power outages. Technological advancements in solar panels, batteries, and LED lighting continue to improve efficiency and reliability, making solar street lights a sustainable choice for the future.
Recyclability
Solar street lights also provide strong environmental benefits through high recyclability. Most components of solar street lights, such as photovoltaic panels and LED modules, are highly recyclable. The table below compares the recyclability of solar lighting components to those of traditional lighting:
|
Component |
Solar Light Recyclability (%) |
Traditional Lighting Recyclability |
|---|---|---|
|
Solar Panels |
99 |
Low / Non-recyclable materials |
|
LED Modules |
95 |
Typically less recyclable |
|
Batteries |
65–84 |
Contains hazardous substances |
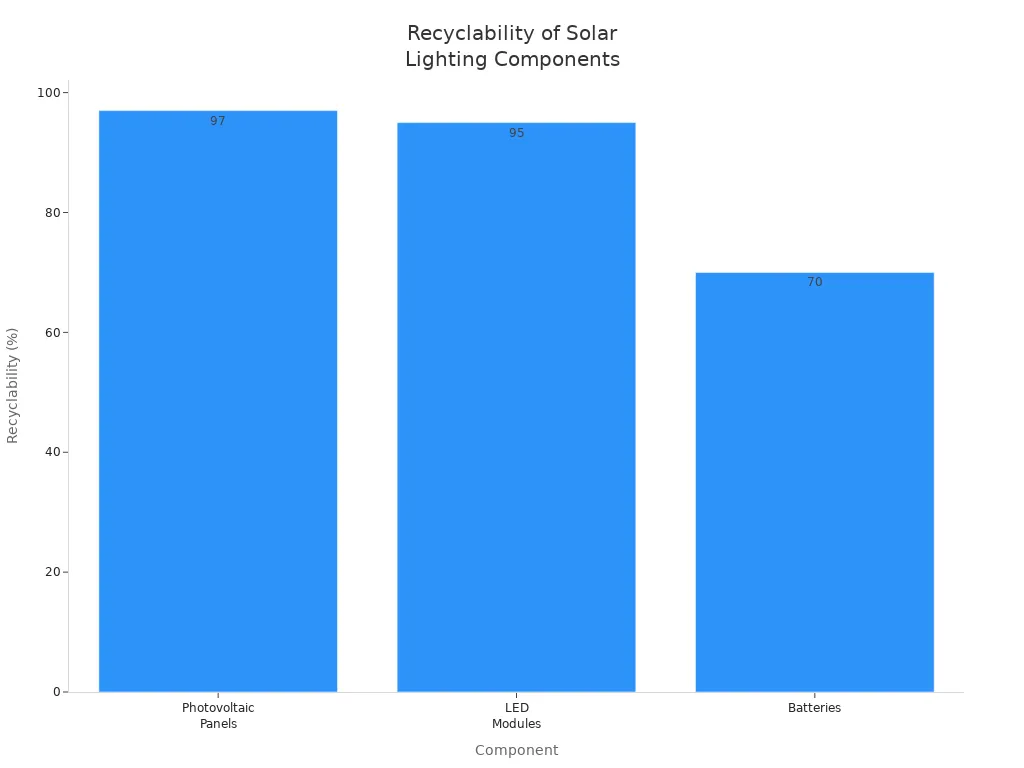
Solar street lights use materials that reduce landfill waste and environmental impact. Traditional lighting products often contain hazardous substances and are less recyclable, increasing landfill waste and pollution. By choosing solar street lights, communities support sustainable lighting and help protect the environment for future generations.
Economic Value of Solar Lights

Upfront Costs
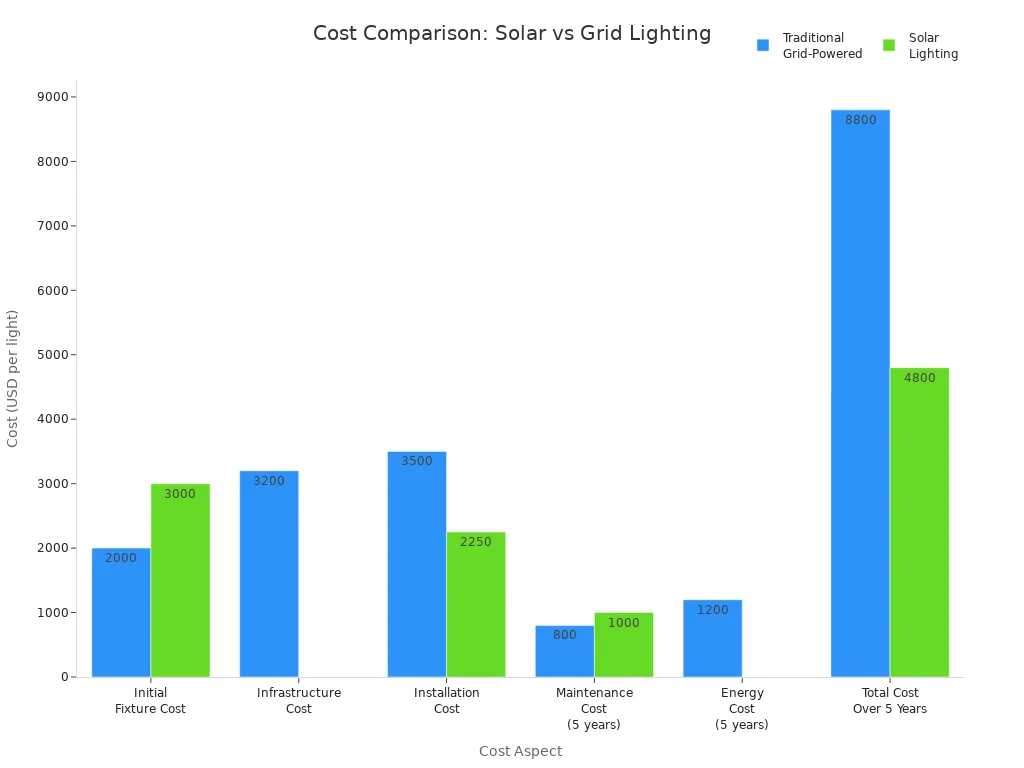
Solar street lights require a different investment structure than traditional lights. The main difference comes from installation. Traditional lights need trenching, wiring, and electrical connections. These steps increase both cost and disruption. Solar street lights do not need trenching or wiring. This makes installation faster and less expensive, especially in new developments or remote areas.
|
Cost Component |
Traditional Grid Lighting (Residential, 50 lights) |
Solar Lighting (50 units) |
|---|---|---|
|
Trenching and Wiring |
$150,000 to $225,000 |
$0 |
|
Equipment (Poles + Fixtures) |
~$125,000 |
Included in unit cost |
|
Unit Cost per Light |
N/A |
~$4,000 |
|
Total Upfront Cost |
$275,000 to $350,000+ |
~$200,000 |
Solar street lights have higher per-unit costs because of solar panels and batteries. However, the elimination of trenching and wiring often results in lower total upfront costs. In commercial projects, solar lighting systems may seem expensive at first, but tax credits and grants can reduce these expenses. Solar lighting also works well in places where traditional lights would need costly infrastructure.
Note: Solar street lights typically cost between $1,850 and $5,000 per unit. Installation is simple and affordable, with no need for grid connection or underground wiring.
Operating Costs
Operating costs play a major role in the total value of a lighting system. Traditional lights use grid electricity, which leads to ongoing energy bills. Solar street lights use free solar energy, so they do not add to electricity costs. This difference creates immediate energy savings.
|
Lighting System Type |
Average Annual Maintenance Cost |
Annual Electricity Cost |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Traditional Street Lights |
~$120 per light |
Significant (varies) |
Frequent bulb replacements every 1-2 years; power supply issues increase costs |
|
Solar Street Lights |
~$50 per light |
$0 |
Maintenance includes inspections and battery upkeep; bulbs last 8-10 years |
Solar street lights require minimal maintenance. Battery replacement happens about every five years. The absence of moving parts reduces the risk of failure. Traditional lights often need frequent bulb changes and wiring repairs, which increase costs. Electricians may be needed for grid-connected lights, adding to expenses.
- Traditional lighting maintenance: about $500 per light each year.
- Solar lighting maintenance: about $100 per light each year.
- Over several years, this difference leads to significant savings.
Solar street lights also help reduce electricity costs and lower energy bills for both municipalities and homeowners. In stadiums, for example, metal halide lights can cost up to $10,000 per year in electricity. Solar stadium lights eliminate this expense.
Long-Term Savings
Solar street lights deliver strong long-term savings. They remove electricity costs entirely, which leads to major energy savings over time. Municipalities that switch to solar street lights see a 60% reduction in public lighting costs. A study of 1.9 million streetlights in 20 major U.S. cities found over $50 million in savings. Solar LED streetlights last two to five times longer than traditional lamps and use 50% less energy, further increasing savings.
Solar street lights also offer a strong return on investment. Payback periods often range from three to seven years. Municipalities benefit from no electricity bills, reduced maintenance, and fewer repairs. Solar street lights use durable, weather-resistant parts that extend their lifespan. These features combine to create lasting value and reliable energy savings.
Real-world examples show that solar street lights eliminate utility bills, trenching, and cabling costs. Cities like Albuquerque and Bartlesville have seen faster deployment and long-term budget relief. Solar systems provide reliable lighting every night, with lower lifetime maintenance than grid-tied systems. When considering installation, energy, and maintenance, solar street lights stand out as a financially superior and sustainable choice.
Tip: Solar street lights help communities achieve energy savings, reduce electricity costs, and lower energy bills while supporting environmental goals.
Energy Efficiency of Solar Lighting
Solar Technology
Solar lighting systems use advanced technology to maximize energy efficiency. Modern solar panels convert sunlight into electricity with high efficiency, even in low-light conditions. Recent advancements have improved the performance of solar panels and batteries, making solar lights more reliable and longer-lasting. Many solar lights now feature:
- High-efficiency solar panels that generate more energy from less sunlight.
- Bifacial and flexible solar panels that capture sunlight from multiple angles and fit various surfaces.
- Motion sensors and automatic on/off sensors that activate lights only when needed, reducing unnecessary energy use.
- Smart technologies, such as IoT and AI, for intelligent lighting control and centralized management.
- Lithium iron phosphate batteries that offer longer life and better safety.
- Self-cleaning solar panels that maintain high energy efficiency with minimal maintenance.
- Eco-friendly materials that enhance sustainability and durability.
These features allow solar lights to deliver consistent, energy-efficient lighting solutions in both urban and rural environments. By using smart controls and efficient components, solar lighting systems reduce energy waste and support sustainable development.
Traditional Lighting
Traditional lighting systems, such as incandescent and halogen bulbs, rely on grid electricity. These lights consume more energy and generate more heat, which leads to higher energy bills and increased carbon emissions. Incandescent bulbs convert only about 20% of the energy they use into light, with the rest lost as heat. In contrast, LED bulbs, commonly used in solar lights, convert 80–90% of energy into light. Traditional lighting also requires frequent maintenance and replacement, which increases both energy consumption and costs over time.
Modern solar lights use LED technology, which consumes significantly less electricity than traditional bulbs. This shift to LEDs has made solar lighting much more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. Solar lights also eliminate the need for wiring and reduce installation complexity, making them a practical choice for many applications.
Performance Metrics
Several key metrics help evaluate the energy efficiency of solar lighting systems:
- Wattage: Measures the energy consumption of the lighting fixture. Lower wattage means less demand on solar panels and batteries.
- Lumens: Indicates the brightness or light output. Higher lumens provide better illumination.
- Luminous Efficacy (Lumens per Watt): Shows how efficiently the system converts energy into visible light.
- Solar Panel Efficiency: Includes power conversion efficiency, temperature coefficient, and degradation rates. These factors determine how much sunlight the panel converts into usable energy and how performance changes over time.
- Real-world Factors: Temperature effects, integration of advanced technologies, and battery performance all influence overall energy efficiency.
Note: Energy-efficient lighting solutions use these metrics to ensure optimal performance and sustainability. Solar lighting systems that score high in these areas provide reliable, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly illumination.
Solar lighting stands out as a leader in energy efficiency. By combining advanced solar technology, efficient LEDs, and smart controls, these systems offer superior energy savings and long-term value compared to traditional lighting.
Solar Street Lights: Real-World Impact
Urban and Rural Cases
Solar street lights have transformed both urban and rural communities by providing reliable lighting and supporting economic growth. Many cities and towns have adopted solar street lights to improve safety, reduce costs, and promote sustainability. The following examples highlight the impact of solar street lights in different settings:
- Dhaka, Bangladesh installed solar street lights, which led to decreased crime rates and increased evening activities. Residents felt safer, and local businesses benefited from longer operating hours.
- Schools in Uganda used solar street lights to extend study hours. Students achieved better academic performance because they could study after dark.
- Medellín, Colombia saw improved security and visibility after installing solar street lights. Local businesses experienced growth as more people visited public spaces at night.
- In Nairobi and Manila, solar street lights extended business hours and attracted more customers. Local economies grew as foot traffic increased in well-lit areas.
- Las Vegas implemented a large-scale solar street lighting project. The city achieved significant annual energy savings and reduced maintenance costs due to the long lifespan of LED technology.
- Princeton, Texas installed 37 off-grid solar-powered LED street lights. Nighttime visibility and safety improved for both pedestrians and motorists. The project also enhanced sustainability by using renewable energy.
- India launched a major initiative, installing over 76,000 solar street lights across 800 villages in Uttar Pradesh and additional units in Manipur. These lights provided reliable illumination in areas without grid access.
- Guinea completed a nationwide campaign, installing 30,000 solar street lights in more than 300 towns and villages. Communities gained safer streets and lower lighting costs.
- Zimbabwe installed 10,000 solar-powered streetlights in Harare, improving road safety and reducing crime.
- Brazil placed over 4,300 solar street lighting poles along a major highway in Rio de Janeiro, increasing safety for drivers and pedestrians.
These cases show that solar street lights address light poverty, support education, and drive economic development in both urban and rural environments.
Cost and Emission Savings
Solar street lights deliver strong financial and environmental benefits. Municipalities report savings of up to 50–70% on combined energy and maintenance costs after switching to solar street lights. These savings come from eliminating electricity bills, as solar street lights operate independently of the grid. Maintenance costs also decrease because LED bulbs and durable batteries last longer and require fewer replacements.
Solar street lights help cities and towns reduce their carbon emissions by replacing fossil-fuel-based electricity with renewable solar energy. Municipal officials recognize that solar street lighting arrays add renewable capacity incrementally, which helps meet climate and energy goals. These projects support cleaner, safer communities and align with broader sustainability strategies.
Federal and state policies, such as the Investment Tax Credit and California’s Net Energy Metering, have accelerated solar adoption in major U.S. cities. Declining solar panel costs and innovations in storage and energy management have made solar street lights more accessible. Over 4 million solar installations now contribute to environmental sustainability and economic opportunities in urban settings.
Note: Solar street lights provide reliable lighting, reduce energy costs, and support climate action. Communities benefit from safer streets, lower expenses, and a cleaner environment.
Outdoor Solar Light Posts: Practical Benefits
Installation
Outdoor solar light posts offer a straightforward installation process that sets them apart from traditional lighting. Most models require only placement in a sunny location, without the need for electrical wiring or trenching. This simplicity reduces both labor and infrastructure costs. The installation of solar light posts often allows for do-it-yourself projects, making them accessible for homeowners and small businesses.
Key steps for installing outdoor solar light posts include:
- Selecting a location that receives at least six hours of sunlight daily.
- Preparing the ground to ensure it is level and free of obstructions.
- Assembling the light post according to manufacturer instructions.
- Securing the post with mounting brackets or stakes.
- Testing the light to confirm it activates at dusk.
Traditional lighting systems require complex planning, professional installation, and extensive wiring. These steps increase both cost and installation time. Outdoor solar light posts eliminate these barriers, making them ideal for rapid deployment in urban, rural, and remote areas. Technological advancements in batteries, LEDs, and solar panels continue to improve reliability, even in areas with seasonal weather changes. Education and awareness campaigns also help communities understand the benefits and address concerns about performance in low sunlight.
Maintenance
Outdoor solar light posts require minimal maintenance compared to traditional lighting systems. They use durable LED fixtures and weather-resistant materials, which extend their lifespan and reduce the need for frequent servicing. The main maintenance tasks involve cleaning the solar panels to remove dirt and debris and replacing rechargeable batteries every five to ten years.
Solar street lights do not rely on complex wiring, so they experience fewer electrical faults. Many models feature smart technology, such as motion sensors and automatic brightness adjustment, which optimize energy use and extend battery life. In contrast, traditional lighting systems demand regular bulb replacements and more complex electrical maintenance. These requirements increase both costs and downtime. Outdoor solar light posts are designed to last 15 to 25 years, with most components requiring little attention. This durability makes them a cost-effective and reliable choice for long-term energy savings.
Security and Versatility
Outdoor solar light posts enhance security and offer versatile lighting solutions for a wide range of environments. They provide reliable illumination for urban streets, residential areas, parks, parking lots, and remote locations. By operating independently of the electrical grid, solar street lights ensure continuous lighting even during power outages or emergencies. This independence improves safety for pedestrians, cyclists, and motorists by reducing dark areas and deterring intruders.
Features such as dusk-to-dawn automatic operation and motion sensors increase safety by activating lights when needed. Outdoor solar light posts can be installed in diverse settings, from residential neighborhoods to public venues, without the limitations of grid power. Their flexibility allows for deployment in off-grid and developing areas, supporting both public and private needs. Solar bollards, a type of solar street light, offer additional benefits with their durable, weather-resistant design and low maintenance requirements. These qualities support sustainable urban development and help guide pedestrians and vehicles safely.
Tip: Outdoor solar light posts combine energy efficiency, easy installation, and enhanced security, making them a practical solution for modern lighting needs.
Incentives and Certifications
Government Programs
Government programs play a key role in making solar lighting more affordable and accessible. Many states and federal agencies offer incentives that reduce the cost of installing solar lights. These programs help homeowners, businesses, and communities adopt clean energy solutions.
- Massachusetts provides performance-based incentives through the SMART program, property tax exemptions, and bonuses for solar battery integration.
- Connecticut offers direct rebates through the Residential Solar Investment Program (RSIP), with higher rates for moderate- and low-income households.
- Maryland’s Solar Access Program (MSAP) gives rebates up to $7,500, based on income eligibility.
- The federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) allows a 30% tax credit on solar system costs for installations between 2022 and 2032.
- Many states offer sales tax exemptions and property tax exemptions to lower both upfront and long-term costs.
- Net metering policies credit solar owners for extra energy produced, which lowers future electric bills.
- Performance-Based Incentives (PBIs) pay solar owners for each kilowatt-hour of electricity generated.
- Subsidized loans from states, utilities, or organizations help finance solar installations.
- Solar Renewable Energy Certificates (SRECs) provide extra income by selling clean energy credits to utilities.
- Community solar projects allow multiple households to share a solar array, reducing individual costs and increasing access.
- Non-profit organizations like GRID Alternatives and Solar United Neighbors offer free or subsidized solar installations, education, and advocacy.
Tip: Resources such as the Database of State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency (DSIRE) help users find up-to-date local incentives.
Carbon Credits
Carbon credit programs reward solar lighting projects for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. These programs create financial incentives for using clean energy instead of fossil fuels.
- Solar PV projects, including solar lighting, generate carbon credits by replacing fossil fuel-based electricity and lowering emissions.
- Projects register with recognized standards such as Verra's Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) or the Gold Standard.
- Monitoring systems track electricity generated and calculate emission reductions using regional grid emission factors.
- Third-party verification ensures data accuracy and confirms emission reductions meet strict standards.
- Verified carbon credits are sold in carbon markets, providing extra revenue for solar lighting projects.
MicroEnergy Credits (MEC) in Kenya and Uganda uses carbon finance to make solar lighting affordable for low-income households. The program partners with microfinance institutions, tracks emission reductions, and ensures that projects would not happen without carbon credit support. This approach lowers costs for clients and encourages wider adoption of solar lighting.
Environmental Certifications
Environmental certifications confirm that solar lighting products meet high standards for safety, durability, and sustainability. These certifications help buyers identify reliable and eco-friendly products.
- MCS certification in the UK assures quality for microgeneration technologies and is required for government incentives. Products must pass tests for temperature cycling, humidity, mechanical loading, and hail impact.
- Intertek certification covers electrical safety, energy efficiency, and compliance with international standards such as ANSI/UL 1598, ANSI/UL 8750, and the IECEE CB Scheme. It also verifies compliance with environmental regulations like RoHS 2.
- UL 8801 certification focuses on photovoltaic luminaire systems, testing batteries, controls, and luminaires as integrated systems. It ensures compliance with IEC/UL 61730 for PV modules and includes streamlined battery testing.
- Energy efficiency certifications such as Energy Star and the DesignLights Consortium require performance and efficiency testing.
Note: These certifications ensure that solar lighting products are safe, reliable, and environmentally responsible, supporting the shift toward sustainable lighting solutions.
Addressing Solar Lighting Concerns
Weather and Sunlight
Solar lighting systems rely on sunlight to generate electricity, so weather conditions play a significant role in their performance. Cloud cover, shading, and seasonal changes can reduce the amount of sunlight available, which lowers charging efficiency and may shorten light duration at night. Temperature extremes also affect system reliability. High heat can decrease battery performance, while cold weather can limit battery charge capacity. Humidity and rainfall may cause corrosion if the system lacks proper waterproofing, but rain can also help by cleaning dust from solar panels. Wind cools panels and can improve efficiency, but strong winds or hail may cause physical damage if the system is not robust.
|
Weather Condition |
Monocrystalline Panels |
Polycrystalline Panels |
Thin-Film Panels |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Sunny Days |
Highest efficiency |
High efficiency |
Good performance |
|
Cloudy Days |
Best low-light output |
Moderate output |
Can outperform others |
|
Rain |
Reduced efficiency |
Slightly lower output |
More prone to damage |
|
Snow |
Performs well in cold |
Slightly less efficient |
Less efficient in cold |
|
Heat |
Efficiency decreases |
More sensitive to heat |
Best in high temps |
|
Wind |
Cooling improves efficiency |
Similar benefits |
More wind damage risk |
|
Hail |
Highly durable |
Durable |
Less durable |
Proper installation and regular maintenance help solar lighting systems withstand these weather challenges. Choosing climate-appropriate materials and adjusting the panel angle and orientation can further improve reliability in different environments.
Initial Investment
The initial investment for solar lighting often raises concerns for buyers. The cost includes equipment, installation, and sometimes site preparation. Many people see the upfront price as higher than traditional lighting. However, the global solar lighting market continues to grow, driven by falling solar panel costs, rising energy prices, and strong government support. Financial incentives such as subsidies, rebates, and tax credits help offset the initial expense.
- The upfront cost covers equipment and installation.
- Long-term savings result from using free solar energy.
- Maintenance costs remain low due to durable LEDs and solar panels.
- Solar lighting can boost property value and sustainability.
- Project phases—assessment, design, procurement, installation, and monitoring—help manage costs.
- Working with a lighting designer ensures efficient system design.
- Tax incentives and rebates further improve financial returns.
Financing options, such as loans or partnerships, make solar lighting more accessible. Over time, reduced energy bills and lower maintenance costs provide a strong return on investment.
Technology Advances
Recent technological advances have made solar lighting more efficient and affordable. Manufacturers now use high-efficiency photovoltaic cells, such as monocrystalline and polycrystalline silicon, which convert more sunlight into electricity. Thin-film solar cells offer lightweight and flexible options for unique applications. Improvements in battery technology, especially high-capacity lithium-ion batteries, increase energy storage and system reliability.
- Modern solar panels perform well even in low-light conditions.
- Advanced battery management systems optimize charging and extend battery life.
- LED technology now produces brighter light with less energy use and longer lifespans.
- Smart features, such as motion sensors and remote controls, help conserve energy and improve user convenience.
- Mass production and increased competition have lowered prices, making solar lighting more affordable for homes, businesses, and public spaces.
These innovations allow solar lighting to deliver reliable performance in a wide range of climates and applications, making it a practical solution for modern lighting needs.
Solar street lights deliver clear environmental and economic benefits. They reduce greenhouse gas emissions, lower air pollution, and support global sustainability goals. Communities, businesses, and individuals gain long-term savings by eliminating electricity bills and reducing maintenance costs. Solar street lights also enhance safety, property values, and urban aesthetics.
For those interested in adopting solar street lights, experts recommend assessing site conditions, exploring government incentives, and working with lighting specialists to design effective solutions. These steps help maximize the benefits and ensure reliable, sustainable lighting for years to come.
FAQ
What makes solar lights more environmentally friendly than traditional lights?
Solar lights use renewable energy from the sun. They do not produce emissions during operation. Traditional lights rely on grid electricity, which often comes from fossil fuels. This difference helps solar lights reduce carbon footprints.
What are the main cost savings with solar lighting?
Solar lighting eliminates electricity bills. Maintenance costs remain low because LEDs and batteries last longer. Installation does not require trenching or wiring. Over time, these factors create significant savings for homeowners and communities.
What is the typical lifespan of a solar street light?
Most solar street lights last 15 to 25 years. LED bulbs and solar panels have long lifespans. Batteries may need replacement every 5 to 10 years. Regular cleaning and inspections help maximize performance.
What incentives exist for installing solar lights?
Many governments offer tax credits, rebates, and grants for solar lighting projects. These incentives lower upfront costs and improve return on investment. Programs vary by location, so users should check local resources.
What maintenance do solar lights require?
Solar lights need occasional cleaning of panels and periodic battery checks. Most systems require little attention. LED bulbs rarely need replacement. This low-maintenance design reduces long-term costs.
What happens to solar lights during cloudy or rainy weather?
Solar lights store energy in batteries during sunny periods. On cloudy or rainy days, they use stored energy to operate. High-quality systems provide reliable lighting for several nights without sunlight.
What are the main components of a solar light system?
|
Component |
Function |
|---|---|
|
Solar Panel |
Captures sunlight |
|
Battery |
Stores energy |
|
LED Fixture |
Provides illumination |
|
Controller |
Manages charging and use |
Each part works together to deliver efficient, off-grid lighting.

